Being a ‘frequent customer’ personally who has visited the dental clinic multiple times since last summer, I am officially getting a dental implant. From a patient’s point of view, during the whole process, all I have to do was visit a dental imaging clinic, stay still in front of a 360 X-ray scanner, lay down with local anaesthesia and after some carpenter works, the titanium implant is planted in my jawbone. As being personally also working in an implant-related field for my PhD, I want to reveal some details about digital implant design that the patient may not know or be informed of.
Step 1:
Scans of the patient can be taken by either a CBCT scanner (Cone Beam Computed Tomography) or an intra-oral scanner. The data was obtained and saved in an STL format and imported into the professional software for data alignment.

Step 2:
The data was obtained and saved in an STL format and imported into the virtual implant planning software for data alignment. The specialists and technicians visualize the implant and start prosthetic planning via the CAD process. The surgical guide and prosthetic components involved are also designed with the software.
3Shape Implant Studio – an example of implant planning software
Step 3:
The manufacturing method of implants and surgical guides can either be subtractive like computer numerical control [CNC] machining; milling or additive i.e. 3D printing, for example, stereolithography (SLA), digital light projection (DLP), jet printing (PolyJet®/ProJet®), and direct laser sintering (DLMS)/selective laser sintering (SLS).
Step 4:
Now the “Best” part, the surgery! Just joking.
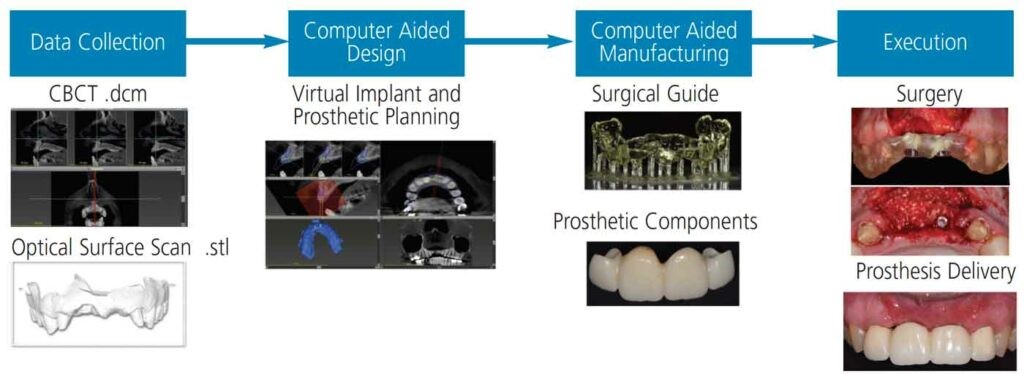
The digital workflow has sped up the treatment process and improved the accuracy of implant design and dental implant placement, which have led to more successful implant surgeries.
References:
[1] https://pocketdentistry.com/digital-workflow-in-implant-dentistry/
[2] https://decisionsindentistry.com/article/utilizing-digital-workflow-implant-treatment-%E2%80%A8planning/
[3] https://www.cavendishimaging.com/cbct/specialist-dentistry/dental-implant-planning/ (Header Image)

This post was written by Esperanza Shi as part of an ongoing series of scientific communications written and curated by BioTrib’s Early Stage Researchers.
Esperanza is researching the Optimisation of Scanning Strategies for 3D Printed Artificial Joints at Imperial College London, UK.
